如何微调SAM模型:从环境配置到训练实现的完整指南
如何微调SAM模型:从环境配置到训练实现的完整指南
- 如何微调SAM模型:从环境配置到训练实现的完整指南
- 引言
- 目录
- 1. 环境配置
- 2. 项目结构
- 3. 数据准备
- 4. 模型微调
- 4.1 数据集类实现
- 4.2 训练函数实现
- 5. 训练过程
- 6. 注意事项和优化建议
- 7. 模型预测和可视化
- 7.1 预测器类实现
- 7.2 可视化函数
- 7.3 使用示例
- 7.4 注意事项
- 7.5 可能的改进
- 结论
- 参考资料
- 快速部署:
引言
Segment Anything Model (SAM) 是 Meta AI 推出的一个强大的图像分割模型。尽管预训练模型表现优秀,但在特定领域(如医疗影像、工业检测等)可能需要进行微调以获得更好的性能。本文将详细介绍如何微调 SAM 模型,包括环境配置、数据准备和训练实现。
目录
- 环境配置
- 项目结构
- 数据准备
- 模型微调
- 训练过程
- 注意事项和优化建议
1. 环境配置
首先,我们需要配置正确的 Python 环境和依赖包。推荐使用虚拟环境来管理依赖:
# 创建并激活虚拟环境
python -m venv sam_env
# Windows:
.\sam_env\Scripts\activate
# Linux/Mac:
source sam_env/bin/activate
# 安装依赖
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
pip install opencv-python
pip install git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything.git
pip install numpy matplotlib
# 下载预训练模型
# Windows PowerShell:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/segment_anything/sam_vit_b_01ec64.pth" -OutFile "sam_vit_b_01ec64.pth"
# Linux/Mac:
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/segment_anything/sam_vit_b_01ec64.pth- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
2. 项目结构
推荐的项目结构如下:
3. 数据准备
为了训练模型,我们需要准备以下数据:
- 训练图像
- 分割掩码
- 边界框标注
以下是数据准备脚本的实现:
import os
import numpy as np
import cv2
from pathlib import Path
def create_project_structure():
"""创建项目所需的目录结构"""
directories = [
'./stamps/images',
'./stamps/masks',
'./checkpoints'
]
for dir_path in directories:
Path(dir_path).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
return directories
def create_sample_data(num_samples=5):
"""创建示例训练数据"""
annotations = []
for i in range(num_samples):
# 创建示例图像
image = np.ones((500, 500, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 255
center_x = np.random.randint(150, 350)
center_y = np.random.randint(150, 350)
radius = np.random.randint(50, 100)
# 绘制对象
cv2.circle(image, (center_x, center_y), radius, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 创建掩码
mask = np.zeros((500, 500), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.circle(mask, (center_x, center_y), radius, 255, -1)
# 保存文件
cv2.imwrite(f'./stamps/images/sample_{i}.jpg', image)
cv2.imwrite(f'./stamps/masks/sample_{i}_mask.png', mask)
# 计算边界框
x1 = max(0, center_x - radius)
y1 = max(0, center_y - radius)
x2 = min(500, center_x + radius)
y2 = min(500, center_y + radius)
annotations.append(f'sample_{i}.jpg,{x1},{y1},{x2},{y2}\n')
# 保存标注文件
with open('./stamps/annotations.txt', 'w') as f:
f.writelines(annotations)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
4. 模型微调
4.1 数据集类实现
首先实现自定义数据集类:
class StampDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, image_dir, mask_dir, bbox_file):
self.image_dir = image_dir
self.mask_dir = mask_dir
self.transform = ResizeLongestSide(1024)
# 加载标注
self.annotations = []
with open(bbox_file, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
img_name, x1, y1, x2, y2 = line.strip().split(',')
self.annotations.append({
'image': img_name,
'bbox': [float(x1), float(y1), float(x2), float(y2)]
})
def __len__(self):
return len(self.annotations)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
ann = self.annotations[idx]
# 加载和预处理图像
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.image_dir, ann['image']))
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
mask = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.mask_dir,
ann['image'].replace('.jpg', '_mask.png')),
cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
mask = mask.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# 图像处理
original_size = image.shape[:2]
input_image = self.transform.apply_image(image)
input_image = input_image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
input_image = torch.from_numpy(input_image).permute(2, 0, 1)
# 标准化
mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).view(-1, 1, 1)
std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).view(-1, 1, 1)
input_image = (input_image - mean) / std
# 处理边界框和掩码
bbox = self.transform.apply_boxes(np.array([ann['bbox']]), original_size)[0]
bbox_torch = torch.tensor(bbox, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(0)
mask_torch = torch.from_numpy(mask).float().unsqueeze(0)
return {
'image': input_image.float(),
'original_size': original_size,
'bbox': bbox_torch,
'mask': mask_torch
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
4.2 训练函数实现
训练函数的核心实现:
def train_sam(
model_type='vit_b',
checkpoint_path='sam_vit_b_01ec64.pth',
num_epochs=10,
batch_size=1,
learning_rate=1e-5
):
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 初始化模型
sam_model = sam_model_registry[model_type](checkpoint=checkpoint_path)
sam_model.to(device)
# 准备数据和优化器
dataset = StampDataset(image_dir='./stamps/images',
mask_dir='./stamps/masks',
bbox_file='./stamps/annotations.txt')
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(sam_model.mask_decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
total_loss = 0
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
# 准备数据
input_image = batch['image'].to(device)
original_size = batch['original_size']
bbox = batch['bbox'].to(device)
gt_mask = batch['mask'].to(device)
# 前向传播
with torch.no_grad():
image_embedding = sam_model.image_encoder(input_image)
sparse_embeddings, dense_embeddings = sam_model.prompt_encoder(
points=None,
boxes=bbox,
masks=None,
)
# 生成预测
mask_predictions, _ = sam_model.mask_decoder(
image_embeddings=image_embedding,
image_pe=sam_model.prompt_encoder.get_dense_pe(),
sparse_prompt_embeddings=sparse_embeddings,
dense_prompt_embeddings=dense_embeddings,
multimask_output=False,
)
# 后处理
upscaled_masks = sam_model.postprocess_masks(
mask_predictions,
input_size=input_image.shape[-2:],
original_size=original_size[0]
).to(device)
binary_masks = torch.sigmoid(upscaled_masks)
# 计算损失并优化
loss = loss_fn(binary_masks, gt_mask)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 10 == 0:
print(f'Epoch: {epoch}, Batch: {batch_idx}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
# 输出epoch统计
avg_loss = total_loss / len(dataloader)
print(f'Epoch {epoch} completed. Average Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}')
# 保存检查点
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
checkpoint_file = f'./checkpoints/sam_finetuned_epoch_{epoch+1}.pth'
torch.save(sam_model.state_dict(), checkpoint_file)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
5. 训练过程
完整的训练过程如下:
- 准备环境和数据:
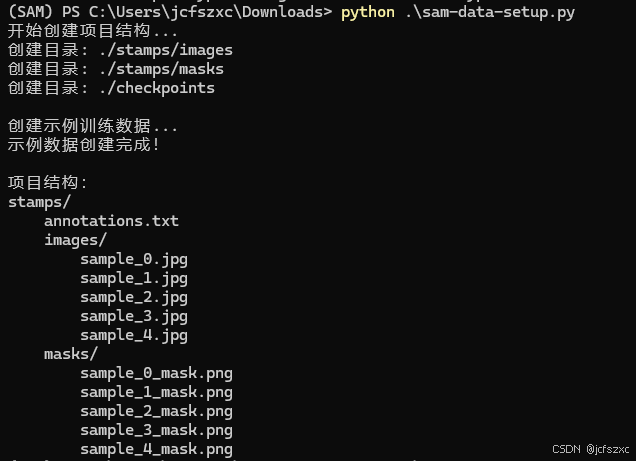
- 开始训练:
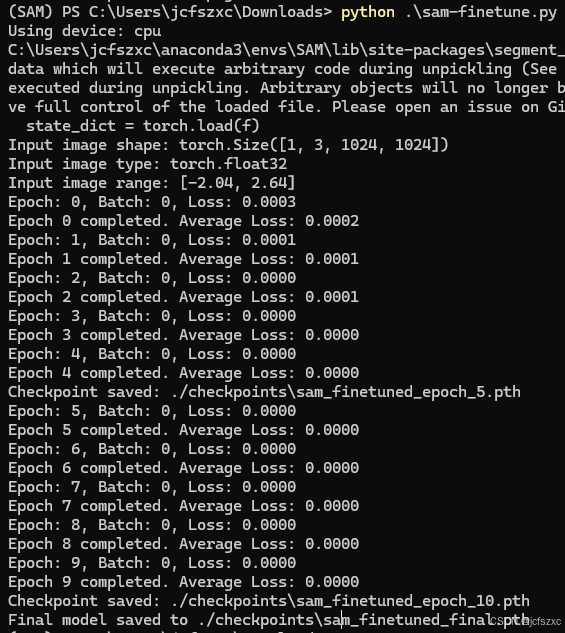
6. 注意事项和优化建议
- 数据预处理:
- 确保图像数据类型正确(float32)
- 进行适当的数据标准化
- 注意图像尺寸的一致性
- 训练优化:
- 根据GPU内存调整batch_size
- 适当调整学习率
- 考虑使用学习率调度器
- 添加验证集评估
- 实现早停机制
- 可能的改进:
- 添加数据增强
- 使用不同的损失函数
- 实现多GPU训练
- 添加训练过程可视化
- 实现模型验证和测试
7. 模型预测和可视化
在完成模型微调后,我们需要一个方便的方式来使用模型进行预测并可视化结果。以下是完整的实现:
7.1 预测器类实现
首先,我们封装一个预测器类,用于处理模型加载、图像预处理和预测:
class SAMPredictor:
def __init__(self, checkpoint_path, model_type="vit_b", device="cuda"):
self.device = torch.device(device if torch.cuda.is_available() and device == "cuda" else "cpu")
self.sam_model = sam_model_registry[model_type](checkpoint=checkpoint_path)
self.sam_model.to(self.device)
self.transform = ResizeLongestSide(1024)- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
这个类提供了简单的接口来加载模型并进行预测。主要功能包括:
- 模型加载和设备配置
- 图像预处理
- 掩码预测
- 后处理优化
7.2 可视化函数
为了better展示预测结果,我们实现了一个可视化函数:
这个函数可以同时显示:
- 原始图像(带边界框)
- 预测的分割掩码
- 结果叠加视图
7.3 使用示例
以下是如何使用这些工具的完整示例:
# 初始化预测器
predictor = SAMPredictor("./checkpoints/sam_finetuned_final.pth")
# 读取测试图像
image = cv2.imread("test_image.jpg")
bbox = [x1, y1, x2, y2] # 边界框坐标
# 预测
mask, confidence = predictor.predict(image, bbox)
# 可视化
visualize_prediction(image, mask, bbox, confidence, "result.png")- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
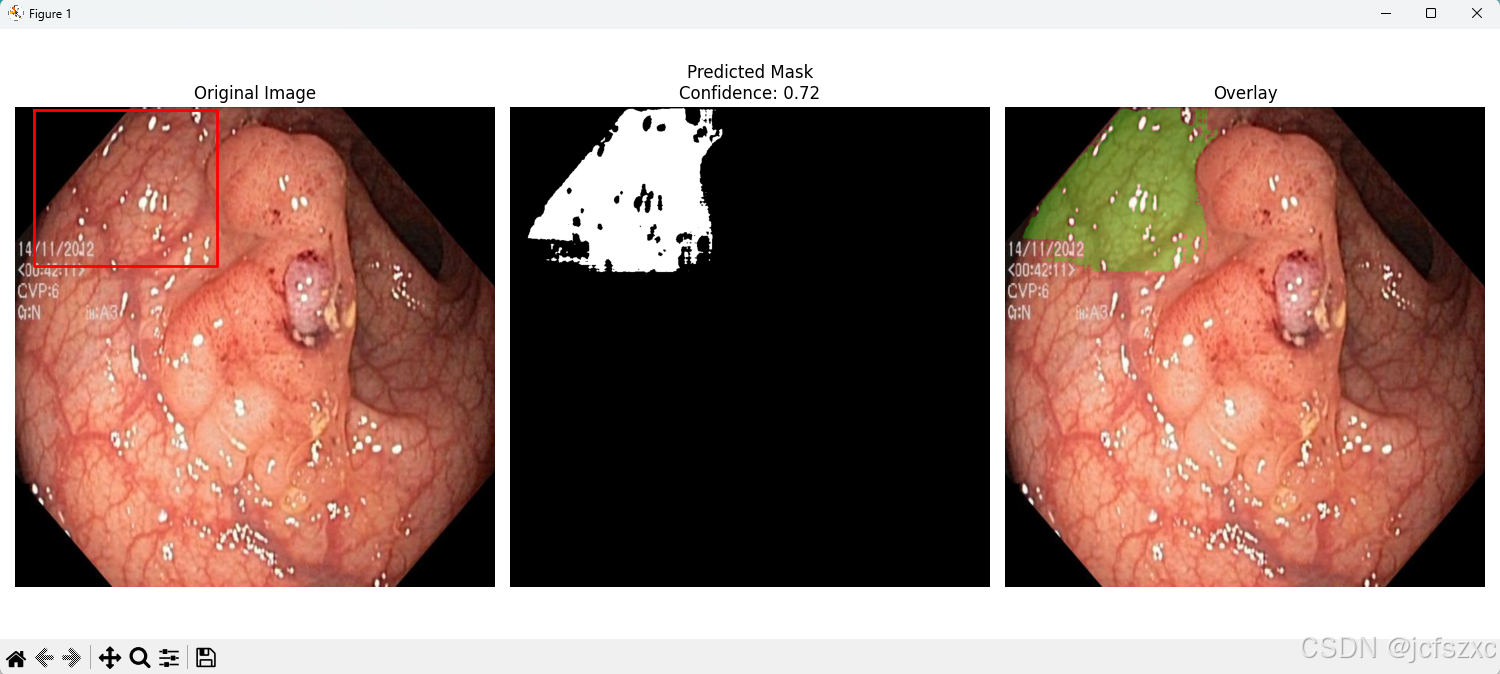
7.4 注意事项
在使用预测器时,需要注意以下几点:
- 输入图像处理:
- 确保图像格式正确(RGB)
- 注意图像尺寸的一致性
- 正确的数据类型和范围
- 边界框格式:
- 使用 [x1, y1, x2, y2] 格式
- 确保坐标在图像范围内
- 坐标值为浮点数
- 性能优化:
- 批处理预测
- GPU 内存管理
- 结果缓存
7.5 可能的改进
- 批量处理功能:
- 多边界框支持:
- 交互式可视化:
def interactive_visualization(image, predictor):
def onclick(event):
if event.button == 1: # 左键点击
bbox = [event.xdata-50, event.ydata-50,
event.xdata+50, event.ydata+50]
mask, _ = predictor.predict(image, bbox)
visualize_prediction(image, mask, bbox)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(image)
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('button_press_event', onclick)
plt.show()- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
这些工具和示例可以帮助你更好地理解和使用微调后的SAM模型。根据具体需求,你可以进一步优化和扩展这些功能。
结论
通过以上步骤,我们实现了SAM模型的微调过程。这个实现可以作为基础,根据具体需求进行优化和改进。在实际应用中,可能需要根据具体任务调整数据预处理、损失函数和训练策略。
建议在使用时注意以下几点:
- 确保训练数据质量
- 合理设置训练参数
- 定期保存检查点
- 监控训练过程
- 适当使用数据增强
希望这个教程对你的项目有所帮助!如果有任何问题,欢迎讨论和交流。
参考资料
- Segment Anything 官方仓库
- PyTorch 文档
- SAM 论文:Segment Anything
- torchvision 文档
快速部署:
下载这三个代码,配置好运行环境,依次运行:
# sam-data-setup.py
import os
import numpy as np
import cv2
from pathlib import Path
def create_project_structure():
"""创建项目所需的目录结构"""
# 创建主目录
directories = [
'./stamps/images',
'./stamps/masks',
'./checkpoints'
]
for dir_path in directories:
Path(dir_path).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
return directories
def create_sample_data(num_samples=5):
"""创建示例训练数据"""
# 创建示例图像和掩码
annotations = []
for i in range(num_samples):
# 创建示例图像 (500x500)
image = np.ones((500, 500, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 255
# 添加一个示例印章 (随机位置的圆形)
center_x = np.random.randint(150, 350)
center_y = np.random.randint(150, 350)
radius = np.random.randint(50, 100)
# 绘制印章
cv2.circle(image, (center_x, center_y), radius, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 创建对应的掩码
mask = np.zeros((500, 500), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.circle(mask, (center_x, center_y), radius, 255, -1)
# 保存图像和掩码
image_path = f'./stamps/images/sample_{i}.jpg'
mask_path = f'./stamps/masks/sample_{i}_mask.png'
cv2.imwrite(image_path, image)
cv2.imwrite(mask_path, mask)
# 计算边界框
x1 = max(0, center_x - radius)
y1 = max(0, center_y - radius)
x2 = min(500, center_x + radius)
y2 = min(500, center_y + radius)
# 添加到注释列表
annotations.append(f'sample_{i}.jpg,{x1},{y1},{x2},{y2}\n')
# 保存注释文件
with open('./stamps/annotations.txt', 'w') as f:
f.writelines(annotations)
def main():
print("开始创建项目结构...")
directories = create_project_structure()
for dir_path in directories:
print(f"创建目录: {dir_path}")
print("\n创建示例训练数据...")
create_sample_data()
print("示例数据创建完成!")
print("\n项目结构:")
for root, dirs, files in os.walk('./stamps'):
level = root.replace('./stamps', '').count(os.sep)
indent = ' ' * 4 * level
print(f"{indent}{os.path.basename(root)}/")
sub_indent = ' ' * 4 * (level + 1)
for f in files:
print(f"{sub_indent}{f}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
# sam-finetune.py
import torch
import numpy as np
from segment_anything import sam_model_registry, SamPredictor
from segment_anything.utils.transforms import ResizeLongestSide
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import cv2
import os
class StampDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, image_dir, mask_dir, bbox_file):
self.image_dir = image_dir
self.mask_dir = mask_dir
self.transform = ResizeLongestSide(1024) # SAM default size
# Load bbox annotations
self.annotations = []
with open(bbox_file, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
img_name, x1, y1, x2, y2 = line.strip().split(',')
self.annotations.append({
'image': img_name,
'bbox': [float(x1), float(y1), float(x2), float(y2)]
})
def __len__(self):
return len(self.annotations)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
ann = self.annotations[idx]
# Load image
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.image_dir, ann['image']))
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Load mask
mask_name = ann['image'].replace('.jpg', '_mask.png')
mask = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.mask_dir, mask_name), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
mask = mask.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# Prepare image
original_size = image.shape[:2]
input_image = self.transform.apply_image(image)
# Convert to float32 and normalize to 0-1 range
input_image = input_image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# Convert to tensor and normalize according to ImageNet stats
input_image = torch.from_numpy(input_image).permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
# Apply ImageNet normalization
mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).view(-1, 1, 1)
std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).view(-1, 1, 1)
input_image = (input_image - mean) / std
# Prepare bbox
bbox = self.transform.apply_boxes(np.array([ann['bbox']]), original_size)[0]
bbox_torch = torch.tensor(bbox, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(0)
# Prepare mask
mask_torch = torch.from_numpy(mask).float().unsqueeze(0)
return {
'image': input_image.float(), # ensure float tensor
'original_size': original_size,
'bbox': bbox_torch,
'mask': mask_torch
}
def train_sam(
model_type='vit_b',
checkpoint_path='sam_vit_b_01ec64.pth',
image_dir='./stamps/images',
mask_dir='./stamps/masks',
bbox_file='./stamps/annotations.txt',
output_dir='./checkpoints',
num_epochs=10,
batch_size=1,
learning_rate=1e-5
):
# Setup device
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f"Using device: {device}")
# Initialize model
sam_model = sam_model_registry[model_type](checkpoint=checkpoint_path)
sam_model.to(device)
# Prepare dataset
dataset = StampDataset(image_dir, mask_dir, bbox_file)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
# Setup optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(sam_model.mask_decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# Loss function
loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# Training loop
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
total_loss = 0
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
# Move inputs to device
input_image = batch['image'].to(device)
original_size = batch['original_size']
bbox = batch['bbox'].to(device)
gt_mask = batch['mask'].to(device)
# Print shapes and types for debugging
if batch_idx == 0 and epoch == 0:
print(f"Input image shape: {input_image.shape}")
print(f"Input image type: {input_image.dtype}")
print(f"Input image range: [{input_image.min():.2f}, {input_image.max():.2f}]")
# Get image embedding (without gradient)
with torch.no_grad():
image_embedding = sam_model.image_encoder(input_image)
# Get prompt embeddings
sparse_embeddings, dense_embeddings = sam_model.prompt_encoder(
points=None,
boxes=bbox,
masks=None,
)
# Generate mask prediction
mask_predictions, iou_predictions = sam_model.mask_decoder(
image_embeddings=image_embedding,
image_pe=sam_model.prompt_encoder.get_dense_pe(),
sparse_prompt_embeddings=sparse_embeddings,
dense_prompt_embeddings=dense_embeddings,
multimask_output=False,
)
# Upscale masks to original size
upscaled_masks = sam_model.postprocess_masks(
mask_predictions,
input_size=input_image.shape[-2:],
original_size=original_size[0]
).to(device)
# Convert to binary mask
binary_masks = torch.sigmoid(upscaled_masks)
# Calculate loss
loss = loss_fn(binary_masks, gt_mask)
# Optimize
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 10 == 0:
print(f'Epoch: {epoch}, Batch: {batch_idx}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
avg_loss = total_loss / len(dataloader)
print(f'Epoch {epoch} completed. Average Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}')
# Save checkpoint
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
checkpoint_file = os.path.join(output_dir, f'sam_finetuned_epoch_{epoch+1}.pth')
torch.save(sam_model.state_dict(), checkpoint_file)
print(f'Checkpoint saved: {checkpoint_file}')
# Save final model
final_checkpoint = os.path.join(output_dir, 'sam_finetuned_final.pth')
torch.save(sam_model.state_dict(), final_checkpoint)
print(f'Final model saved to {final_checkpoint}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create output directory if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs('./checkpoints', exist_ok=True)
# Start training
train_sam()- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
- 172.
- 173.
- 174.
- 175.
- 176.
- 177.
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from segment_anything import sam_model_registry, SamPredictor
from segment_anything.utils.transforms import ResizeLongestSide
import cv2
from pathlib import Path
class SAMPredictor:
def __init__(self, checkpoint_path, model_type="vit_b", device="cuda"):
"""
初始化SAM预测器
Args:
checkpoint_path: 模型权重路径
model_type: 模型类型 ("vit_h", "vit_l", "vit_b")
device: 使用设备 ("cuda" or "cpu")
"""
self.device = torch.device(device if torch.cuda.is_available() and device == "cuda" else "cpu")
print(f"Using device: {self.device}")
# 加载模型
self.sam_model = sam_model_registry[model_type](checkpoint=checkpoint_path)
self.sam_model.to(self.device)
# 创建图像变换器
self.transform = ResizeLongestSide(1024)
def preprocess_image(self, image):
"""预处理输入图像"""
# 确保图像是RGB格式
if len(image.shape) == 2:
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
elif image.shape[2] == 4:
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2RGB)
elif len(image.shape) == 3 and image.shape[2] == 3:
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image = cv2.resize(image, (1024, 1024), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# 保存原始尺寸
original_size = image.shape[:2]
# 调整图像大小
input_image = self.transform.apply_image(image)
# 转换为float32并归一化
input_image = input_image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# 转换为tensor并添加batch维度
input_image = torch.from_numpy(input_image).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
# 标准化
mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).view(-1, 1, 1)
std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).view(-1, 1, 1)
input_image = (input_image - mean) / std
return input_image.to(self.device), original_size
def predict(self, image, bbox):
"""
预测单个图像的分割掩码
Args:
image: numpy array 格式的图像
bbox: [x1, y1, x2, y2] 格式的边界框
Returns:
binary_mask: 二值化的分割掩码
confidence: 预测的置信度
"""
# 预处理图像
input_image, original_size = self.preprocess_image(image)
# 准备边界框
bbox_torch = torch.tensor(bbox, dtype=torch.float, device=self.device).unsqueeze(0)
# 获取图像嵌入
with torch.no_grad():
image_embedding = self.sam_model.image_encoder(input_image)
# 获取提示嵌入
sparse_embeddings, dense_embeddings = self.sam_model.prompt_encoder(
points=None,
boxes=bbox_torch,
masks=None,
)
# 生成掩码预测
mask_predictions, iou_predictions = self.sam_model.mask_decoder(
image_embeddings=image_embedding,
image_pe=self.sam_model.prompt_encoder.get_dense_pe(),
sparse_prompt_embeddings=sparse_embeddings,
dense_prompt_embeddings=dense_embeddings,
multimask_output=False,
)
# 后处理掩码
upscaled_masks = self.sam_model.postprocess_masks(
mask_predictions,
input_size=input_image.shape[-2:],
original_size=original_size
).to(self.device)
# 转换为二值掩码
binary_mask = torch.sigmoid(upscaled_masks) > 0.5
return binary_mask[0, 0].cpu().numpy(), iou_predictions[0, 0].item()
def visualize_prediction(image, mask, bbox, confidence, save_path=None):
"""
可视化预测结果
Args:
image: 原始图像
mask: 预测的掩码
bbox: 边界框坐标
confidence: 预测置信度
save_path: 保存路径(可选)
"""
# 创建图形
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
# 显示原始图像
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.title('Original Image')
# 绘制边界框
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, bbox)
plt.plot([x1, x2, x2, x1, x1], [y1, y1, y2, y2, y1], 'r-', linewidth=2)
plt.axis('off')
# 显示预测掩码
plt.subplot(132)
plt.imshow(mask, cmap='gray')
plt.title(f'Predicted Mask\nConfidence: {confidence:.2f}')
plt.axis('off')
# 显示叠加结果
plt.subplot(133)
overlay = image.copy()
overlay[mask > 0] = overlay[mask > 0] * 0.7 + np.array([0, 255, 0], dtype=np.uint8) * 0.3
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(overlay, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.title('Overlay')
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
if save_path:
plt.savefig(save_path)
print(f"结果已保存到: {save_path}")
plt.show()
def main():
# 配置参数
checkpoint_path = "./checkpoints/sam_finetuned_final.pth" # 使用微调后的模型
test_image_path = "./stamps/images/cju0qx73cjw570799j4n5cjze.jpg"
output_dir = "./predictions"
# 创建输出目录
Path(output_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 初始化预测器
predictor = SAMPredictor(checkpoint_path)
# 读取测试图像
image = cv2.imread(test_image_path)
image = cv2.resize(image, (1024, 1024), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# 读取边界框(这里使用示例边界框,实际应用中可能需要从标注文件读取)
with open('./stamps/annotations.txt', 'r') as f:
first_line = f.readline().strip()
_, x1, y1, x2, y2 = first_line.split(',')
bbox = [float(x1), float(y1), float(x2), float(y2)]
# 进行预测
mask, confidence = predictor.predict(image, bbox)
# 可视化结果
save_path = str(Path(output_dir) / "prediction_result.png")
visualize_prediction(image, mask, bbox, confidence, save_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
- 172.
- 173.
- 174.
- 175.
- 176.
- 177.
- 178.
- 179.
- 180.
- 181.








 已为社区贡献41条内容
已为社区贡献41条内容

所有评论(0)